C语言算法赛——蓝桥杯(省赛试题)
C语言算法赛——蓝桥杯(省赛试题)
版权声明:本文为博主作者:慢了半拍i原创文章,版权归属原作者,如果侵权,请联系我们删除!
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_56641478/article/details/135726057
一、十四届C/C++程序设计C组试题

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++
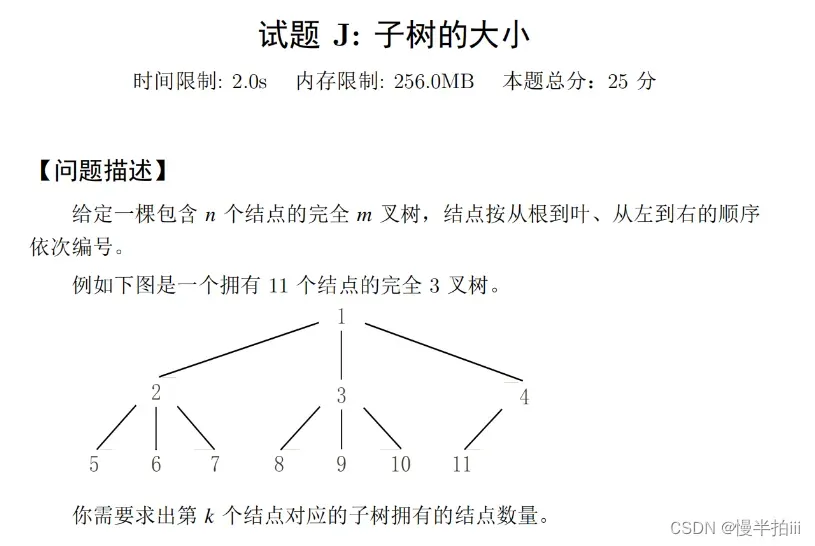
1 | |
C++
二、十四届C/C++程序设计B组试题

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++
三、十四届C/C++程序设计A组试题

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++
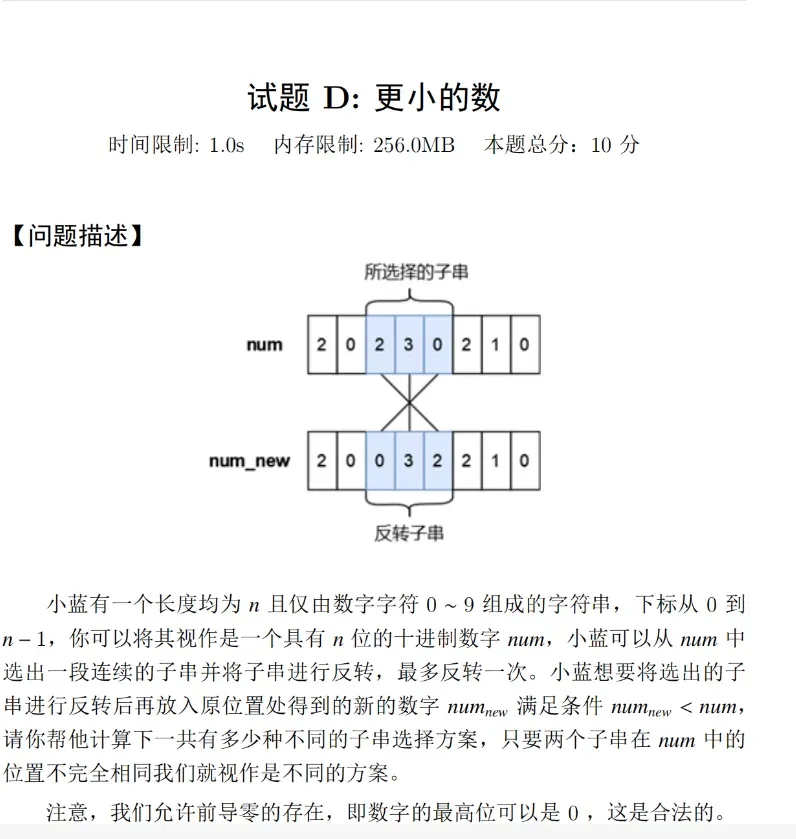
1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++
四、十三届C/C++程序设计C组试题

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++

1 | |
C++
五、十三届C/C++程序设计B组试题
六、十三届C/C++程序设计A组试题
七、十二届C/C++程序设计C组试题
八、十二届C/C++程序设计B组试题
九、十二届C/C++程序设计A组试题
十、十一届C/C++程序设计C组试题
版权声明:本文为博主作者:慢了半拍i原创文章,版权归属原作者,如果侵权,请联系我们删除!
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_56641478/article/details/135726057
C语言算法赛——蓝桥杯(省赛试题)
http://example.com/2024/02/27/C语言算法赛——蓝桥杯(省赛试题)/